To trade forex in the UK, open an account with a trusted, FCA-regulated broker. Deposit funds, then use the trading platform to analyse currency pairs through technical or fundamental analysis. Execute buy or sell orders, and always manage risk using tools like stop-losses and realistic profit targets.
The foreign exchange (forex) market is the world’s largest financial market, with daily trading volumes exceeding $7.5 trillion1.
It offers UK investors access to global currencies and high liquidity, but also carries significant risk.
If you’re ready to begin trading forex, follow these six key steps:
- Select a currency pair – Start with major pairs like EUR/USD or explore exotics such as USD/TRY.
- Choose a trading method – Trade via CFDs, the spot market, or forex futures.
- Open and fund an account – Use an FCA-regulated broker and deposit funds securely.
- Decide to buy or sell – Go long if you expect the base currency to rise, or short if you expect it to fall.
- Manage your risk – Set stop-losses, use leverage cautiously, and trade within your risk tolerance.
- Monitor and close your trade – Track live charts, then close positions to lock in profit or limit loss.
FCA verification requirements for UK forex accounts
All FCA-regulated brokers must verify each client before activating a live trading account.
This ensures compliance with AML and MiFID II standards. When valid documents are uploaded, verification is usually completed within one business day.
Documents required
- Proof of identity (POI): passport, UK/EU driving licence, or national ID card.
- Proof of address (POA): utility bill, bank or credit card statement, or HMRC/council tax letter issued within the last three months.
- Optional income evidence: may be required for high-volume or professional accounts.
Upload format and timeframe
Submit documents in PDF, JPG, or PNG (under 10 MB). Files must be clear, in colour, and uncropped.
- Automatic checks: approval within 5–15 minutes via AI systems.
- Manual review: up to 24 hours if details need verification.
If verification fails
Ensure your name and address match the application. Avoid using work emails or business addresses. Re-upload clearer images or contact the broker’s compliance team if pending beyond one business day.
Forex account types and trading platforms (UK)
Before opening an account, decide which setup matches your trading goals. UK brokers offer several account types that vary by leverage, execution model, and regulation level.
Main account types
| Account Type | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Demo Account | Simulated trades with virtual funds and live prices. | Beginners testing strategies. |
| Standard / CFD Account | Real-money account with variable spreads and leverage up to 1:30. | Retail traders seeking flexibility. |
| Professional Account | Higher leverage (up to 1:200) for eligible clients. | Experienced or institutional traders. |
| Swap-Free (Islamic) Account | Interest-free account with flat admin fees. | Sharia-compliant traders. |
| Corporate Account | Operated under a registered company. | Managed funds and trading firms. |
Trading platform options
- MetaTrader 4 (MT4): Widely used for Expert Advisors and algorithmic trading.
- MetaTrader 5 (MT5): Supports more instruments and faster execution.
- cTrader: Popular with scalpers for Level II pricing and depth-of-market data.
- Proprietary platforms: Broker-built tools like IG Trader or xStation 5 with built-in analytics.
- Mobile apps: Full trading access on iOS and Android for on-the-go management.
Choosing the right setup early prevents migration or re-verification later.
Regulation and safety checks
Only trade with FCA-regulated brokers.
Before registration:
- Confirm licence number on the FCA Financial Services Register.
- Ensure funds are held in segregated Tier-1 bank accounts.
- Verify FSCS protection up to £85,000.
- Review the broker’s Key Information Document (KID) and risk disclosures.
What is the foreign exchange market?
The foreign exchange (forex or FX) market is a global, decentralised marketplace where currencies are traded 24 hours a day, five days a week.
It underpins international trade and investment by allowing individuals, businesses, and institutions to exchange one currency for another. With a daily trading volume of over $7.5 trillion, it is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world.
Forex traders speculate on exchange rate movements between currencies, aiming to profit from price fluctuations while managing risk through leverage limits and stop-loss orders.
Exchange rates and currency pairs
An exchange rate shows how much of one currency is needed to buy another. Rates move constantly due to factors such as interest rates, inflation, economic data, and geopolitical events.
Currencies are traded in pairs, such as GBP/USD, where GBP is the base currency and USD is the quote currency. The rate tells you how many U.S. dollars it takes to buy one British pound.
Understanding how pairs are quoted is essential, as forex trading involves predicting whether the base currency will rise or fall against the quote.
What is the aim of forex trading?
The goal of forex trading is to profit from changes in exchange rates. Traders buy a currency pair if they expect it to rise, or sell it if they expect it to fall.
Profits come from buying low and selling high (or vice versa). Successful traders rely on technical analysis, fundamental analysis, or a combination of both, while using strict risk management to protect capital.
Remember: forex trading is high risk. Use leverage carefully and never trade money you cannot afford to lose.
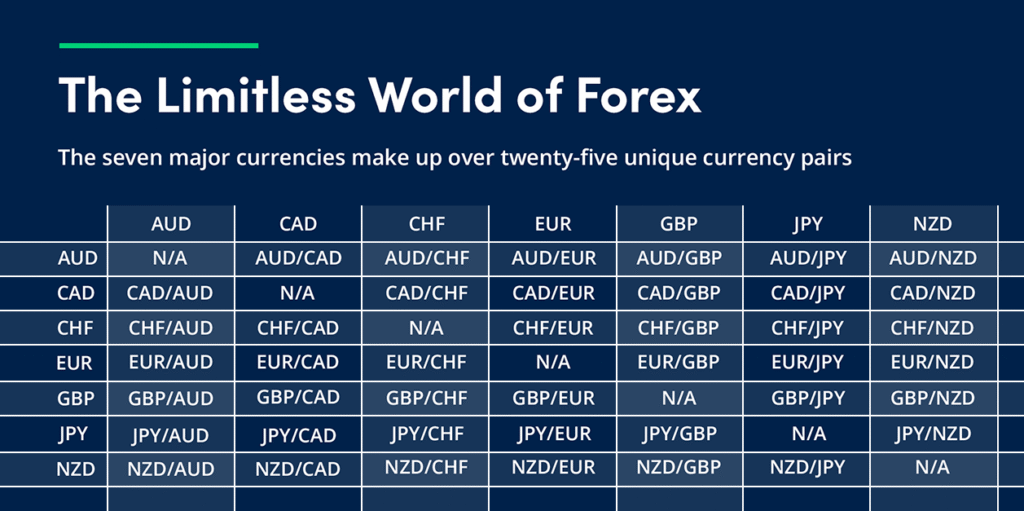
Main currency pairs
Currency pairs fall into three main groups:
| Category | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Major pairs | Include the USD and other leading currencies; highest liquidity and tightest spreads. | EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/JPY, USD/CHF |
| Minor pairs | Crosses between major currencies that exclude USD. | EUR/GBP, GBP/JPY, EUR/JPY |
| Exotic pairs | Combine a major currency with one from an emerging economy; higher volatility and wider spreads. | USD/ZAR, USD/BRL, EUR/TRY |
Majors dominate trading volumes, while exotics offer higher risk and potential reward.
What does the spread mean in forex trading?
The spread is the difference between the bid and ask price of a currency pair. It represents the cost of entering a trade and is usually measured in pips (0.0001).
- Bid price: what buyers are willing to pay.
- Ask price: what sellers are asking.
A narrower spread means lower trading costs. Spreads depend on market liquidity, volatility, and broker pricing. Brokers earn revenue from these spreads, so prices must move beyond the spread before a trade becomes profitable.
What do leverage and margin mean?
Leverage allows you to control a large trade size with a smaller amount of capital. For example, 1:30 leverage lets you trade £30,000 with £1,000 of your own funds. While leverage can increase profits, it also amplifies losses.
Margin is the portion of your capital set aside as collateral for a leveraged trade. If your account balance drops too low, a margin call may occur, requiring additional funds to keep positions open.
Managing leverage responsibly is critical. High leverage increases exposure and can lead to losses exceeding your deposit if not controlled properly.
Key takeaway:
The forex market offers vast opportunities but carries substantial risk. Choose an FCA-regulated broker, start with a demo account, and master concepts like spreads, leverage, and risk control before trading with real capital.
How to trade forex in the UK (step-by-step guide)
Trading forex in the UK is straightforward once you understand the process and follow regulatory best practices.
Below is a simple step-by-step guide to get started safely and effectively.
Step 1: Choose an FCA-regulated forex broker
Select a trusted, FCA-regulated broker to ensure your funds are protected under UK law. FCA regulation guarantees client fund segregation and eligibility for FSCS protection up to £85,000 if the firm becomes insolvent. Compare brokers for fees, spreads, leverage, and available platforms before opening an account.
Step 2: Open and verify your trading account
Complete the broker’s registration form and upload your proof of identity (passport or driving licence) and proof of address (utility bill or bank statement). Verification usually takes under 24 hours. Once approved, you can access a demo or live trading account.
Step 3: Fund your account
Deposit funds using secure payment methods such as Visa, bank transfer, or PayPal. Start small while learning. Most UK brokers have no deposit fees, and minimum deposits typically range from £50 to £250.
Step 4: Select a currency pair and analyse the market
Pick from major, minor, or exotic pairs. Use technical analysis (charts, indicators, price trends) and fundamental analysis (economic data, interest rates, news) to guide your decisions. Always check volatility and spreads before entering a trade.
Step 5: Place your trade (buy or sell)
Decide whether to go long (buy) if you expect the base currency to rise or go short (sell) if you expect it to fall. Enter the trade via your broker’s platform (e.g. MT4, MT5, or cTrader) and specify:
- Position size
- Stop-loss order (to limit losses)
- Take-profit level (to lock in gains)
Step 6: Monitor your trade and manage risk
Track open positions through live charts and broker alerts. Adjust stop-loss levels to protect profit or reduce exposure. Avoid overusing leverage, as it can amplify both gains and losses.
Step 7: Close your position and review performance
Exit your trade manually or when take-profit/stop-loss levels trigger. Review the trade outcome and record key insights to refine your strategy.
Quick tip: Always start with a demo account to practise with virtual funds before trading live. This helps you understand order execution, spreads, and risk control without financial loss.
Forex trading example (EUR/USD)
Here’s a simple example showing how a typical forex trade works.
Currency pair: EUR/USD
Suppose the EUR/USD pair is quoted at a bid of 1.1000 and an ask of 1.1002. The spread (difference between bid and ask) is 0.0002, or 2 pips.
Trade direction: Buy (go long)
You expect the euro to strengthen against the U.S. dollar, so you place a buy order on EUR/USD.
Position size: 1 standard lot = 100,000 units of EUR.
Leverage and margin:
With 50:1 leverage, you only need 1/50th of the trade value as margin.
- Trade size: €100,000
- Required margin: €2,000 (€100,000 ÷ 50)
Execution:
You buy at 1.1002 (ask price).
Market movement:
Later, the price rises to a bid of 1.1050 and an ask of 1.1052. You close your trade at the bid price of 1.1050.
Profit calculation:
Price moved from 1.1002 → 1.1050, a gain of 48 pips.
Each pip in a standard lot of EUR/USD = $10.
- 48 pips × $10 = $480 profit
Your €2,000 margin generated $480, or roughly 24% ROI on the trade.
Key takeaway: This example shows how small currency movements can lead to significant gains—or losses—when leverage is used. While leverage boosts potential returns, it can also magnify losses beyond your initial deposit. Always trade with FCA-regulated brokers, set stop-loss orders, and manage risk carefully.
Choosing a suitable forex broker (UK)
Selecting the right forex broker is one of the most important steps in forex trading.
The best choice combines strong regulation, fair pricing, and reliable trading tools.
1. Regulation and security
Always trade with an FCA-regulated broker. Regulation ensures client fund segregation, fair conduct, and eligibility for FSCS protection up to £85,000. Avoid offshore or unlicensed brokers.
2. Trading platform
Choose a stable, user-friendly platform with real-time charts, analysis tools, and clear order execution. Popular options include MetaTrader 4 (MT4), MetaTrader 5 (MT5), cTrader, or proprietary web platforms such as IG Trader or xStation 5.
3. Range of currency pairs
Look for brokers offering a broad selection of major, minor, and exotic pairs. A wide range allows greater flexibility for different strategies and market conditions.
4. Spreads and commissions
Compare spreads, commissions, and execution speed. Lower spreads reduce trading costs, but ensure the broker also offers reliable order execution and price transparency.
5. Leverage and margin requirements
Under FCA rules, retail traders can access up to 1:30 leverage. Professional clients may qualify for higher limits. Understand margin requirements clearly and use leverage cautiously to avoid magnified losses.
6. Account types and minimum deposit
Check if the broker offers standard, professional, swap-free (Islamic), or demo accounts. Minimum deposits typically range from £50–£250. Choose based on your budget and experience level.
7. Customer support
Reliable 24/5 support is vital during volatile trading hours. Prioritise brokers with live chat, email, and phone assistance that respond quickly and knowledgeably.
8. Education and research tools
Choose brokers that provide market insights, webinars, and tutorials. Strong educational support helps you build long-term trading skills and confidence.
9. Payment methods
Ensure your broker offers secure, fast deposits and withdrawals through methods like Visa, PayPal, or bank transfer. Avoid platforms with unclear withdrawal policies.
10. Reputation and reviews
Research the broker’s track record and trader feedback. Look for consistently positive reviews on reliability, platform stability, and customer service.
Best practices before placing your first trade
Preparation is key to long-term success in forex trading. Before opening a live position, ensure your technical setup, financial plan, and risk controls are in place.
Technical setup
Practise on a demo account until you can open and close trades confidently. Configure charts, indicators, and time zones for clarity. Add an economic calendar and news feed to track key events that affect volatility.
Financial preparation
Deposit only what you can afford to lose. Start with micro-lots (0.01) to limit exposure. Check that pip values and margin settings align with your risk plan.
Risk and execution control
Set default stop-loss and take-profit orders before every trade. Keep total open exposure under 5% of account equity. Avoid trading during major announcements (e.g. Bank of England rate decisions) until you’re comfortable managing volatility.
Post-trade review
Export trade history and calculate average win/loss (expectancy). Keep a trading journal with entry/exit reasons and emotional notes. Identify recurring mistakes before increasing position sizes.
Forex trading strategies
Different strategies suit different risk levels and time commitments. Here are the main approaches used by UK traders:
- Trend trading: Trade in the direction of a strong uptrend or downtrend using tools like moving averages and trendlines.
- Range trading: Buy near support and sell near resistance when prices move within a defined range.
- Breakout trading: Enter when prices break above or below key levels, anticipating strong follow-through.
- Position trading: Long-term approach based on fundamental analysis and major market cycles.
- Scalping: Rapid-fire trades seeking small profits per move; requires low spreads and fast execution.
- Day trading: Open and close all positions within one day to avoid overnight risk.
- Swing trading: Hold trades for days or weeks, capturing medium-term price swings.
Always test strategies on a demo account before committing real funds. Each method carries unique risks and requires discipline and consistency.
Pros and cons of forex trading
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| High liquidity: Easy trade execution with minimal slippage. | High volatility: Sudden moves can lead to sharp losses. |
| 24/5 access: Trade any time across global sessions. | Complex analysis: Requires understanding of global economics and sentiment. |
| Leverage options: Control larger positions with smaller capital. | Magnified risk: Leverage can increase losses as well as gains. |
| Diverse markets: Trade major, minor, or exotic pairs. | Counterparty risk: OTC trading depends on broker reliability. |
Common forex trading fees
Understanding fees helps you manage costs and maximise returns.
- Spreads: The difference between buy (ask) and sell (bid) prices. Narrower spreads mean lower costs.
- Commissions: Some brokers charge a fixed or volume-based fee per trade.
- Swap (rollover) fees: Charged or earned when holding positions overnight, based on interest rate differentials.
- Withdrawal fees: Vary by broker and payment method.
- Inactivity fees: Applied when no trades occur for a set period.
- Currency conversion fees: Apply when trading in a currency different from your account base.
Compare broker fee structures carefully to understand true trading costs before committing.
Final thoughts
Forex trading offers UK investors access to the world’s largest and most liquid financial market, but success depends on preparation, discipline, and risk control.
Start with a demo account, choose an FCA-regulated broker, and focus on learning strategy and money management before trading live.
With the right tools and education, you can trade confidently while keeping risk in check.
FAQs
Is forex trading legal in the UK?
Yes, forex trading is legal in the UK. The Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) is the regulatory body responsible for overseeing forex trading activities and ensuring that brokers and traders comply with the necessary regulations. As long as you trade with a regulated broker and abide by the relevant guidelines, you can engage in forex trading activities in the UK with confidence.
Is forex trading profitable UK?
Forex trading in the UK has the potential to be profitable, as it provides opportunities to capitalise on the fluctuations in currency exchange rates. Traders who have a solid understanding of the market, employ effective strategies, and manage their risks appropriately can achieve profits. However, it’s important to note that forex trading involves inherent risks, and not all traders will be consistently profitable. Success in forex trading requires continuous learning, practice, discipline, and the ability to adapt to changing market conditions.
When is the best time to trade forex UK?
The best time to trade forex in the UK is during the overlap of major trading sessions, such as the London and New York sessions.
Is forex riskier than stocks?
Forex trading and stock trading both carry risks, but the level of risk can vary depending on various factors such as market volatility, leverage usage, and individual trading strategies. It’s essential to thoroughly understand the risks involved in both markets and employ proper risk management techniques.
Can you make money trading forex UK?
Yes, you can make money trading forex in the UK, but it’s important to note that forex trading involves substantial risk and it’s possible to incur significant losses. Success in forex trading depends on a variety of factors, including your understanding of the markets, trading strategy, and risk management practices. It’s advisable to start with a demo account and gain adequate experience before trading with real money.
How do beginners get into forex?
Beginners interested in forex trading typically start by educating themselves on the basics of currency markets, trading strategies, and risk management. The next step is often to open a demo account with a reputable forex broker to practice trading without risking real money. Once comfortable with the trading platform and strategies, beginners can then transition to a live account, deposit funds, and start trading.
Do you get taxed on forex trading UK?
In the UK, forex trading can be subject to taxation, but the specifics depend on your circumstances and how you approach trading. If you are deemed to be trading forex as a form of income, then it may be subject to income tax. However, if you are considered to be trading as a private investor, then any gains might be subject to Capital Gains Tax (CGT). It’s important to consult with a tax advisor to understand the tax implications tailored to your situation.
Is forex trading difficult?
Forex trading can be complex and involves a high level of risk, making it challenging for beginners without proper education and risk management strategies. Success requires a deep understanding of the forex market, trading techniques, and the ability to analyse economic indicators and trends. While it’s not impossible to be profitable, it does take time, discipline, and a well-thought-out approach to mitigate risks and optimise returns.
You may also like:
Sources:




